Potatoes are one of the main food crops in the country. The formation of a large vegetative mass for a short period (60-90 days) and receiving relatively high yields, accompanied by significant biological export of nutrient elements, determines their greater exactingness to the soil nutrient regime [1].
Results from studies indicate that in intensive mineral fertilization, which sharply increase the yields, the nutritional value of the potato the most frequently decreases [2, 3]. It was established that the dry matter and starch content decreases with an increase in nitrogen and potassium fertilizers in comparison with the phosphorus fertilizers [4].
Researches in the field of breeding for development of new potato varieties [5] have conducted in Bulgaria and some agronomic factors associated with potato growing have studied [6, 7]. The researches on the influence of fertilization as one of the main factors are limited. They are aimed mainly for medium early production [8].
MATERIAL AND METHODS. The influence of mineral fertilization on biological manifestations, yield and dry matter content in the potato tuber of variety “Nadejda”, early field production has studied for three years.
Increasing rates for nitrogen were studied: 0, 80, 160 and 240 kg/ha, applied separately and at phosphorus background: 0, 80, 160 and 240 kg/ha and selected variants of the potassium: 0, 80 and 160 kg/ha. It was used ammonium nitrate, triple superphosphate and potassium sulphate. Specified amounts of phosphorus and potassium fertilizers were applied once in preparing of the soil for planting while the nitrogen fertilizer — twofold: in combination with phosphorus and potassium and during the vegetation period with the first hoeing. The experiment was conducted by the block method in four repetitions on a reporting area of 9,6 m2 by 80 x 25 cm scheme.
The strongly leached meadow cinnamon soil is with humus content of 2.1%, pH (H2O) — 6.9 — 7.0; mineral N/NH4-N + NO3-N/ — 1.93 mg/100g soil (defined by distillation); movable P2O5 and K2O (determined by Egner-Riem method) — 27.8 mg and 20.4 mg/100 g soil, respectively.
The indexes of the study: biometric measurements — plant height, number of leaves and tubers per plant, tuber weight; yield; quality — dry matter content in the tubers /weight/. The equations of the curves expressing the relationship between the rate of nitrogen, PK background and yield were determined by regression analysis.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION. It was established that changes in the stem height, and stem weight was related mainly with increase of the rate of nitrogen from 0 to 240 kgN/ha, as the relation is a direct ratio /Table. 1/. The tendency is kept in increased levels of phosphorus. The greatest foliar weight is obtained in fertilization with N240P80 – 273.4 kg/plant.
The results of the yield as the most significant indexes show that it is the highest after fertilization with N160P160K160 – 3 9420 kg/ha, followed by that after fertilization with N160P160K80 – 3 7200 kg/ha, as the increase towards the control is 83.0% and 73.3%, respectively /Table. 1/. The difference between the variants is statistically well proven.
Table 1. Biometric measurements and productivity in potato
|
Varisnts |
Stems | Leaves | Tuberts | |||||
| h | number | massa | number | massa | number | yield |
% |
|
|
cm |
g | g |
kg |
|||||
| N0Р0К0 | 44.5 | 2.9 | 43.5 | 36.9 | 94.4 | 10.3 | 21470 | 100 |
| N80Р0К0 | 54.0 | 3.1 | 80.0 | 46.0 | 132.2 | 12.8 | 28050 | 130.6 |
| N160Р0К0 | 61.3 | 2.6 | 143.0 | 88.0 | 240.1 | 13.9 | 31200 | 145.3 |
| N240Р0К0 | 61.7 | 2.4 | 157.1 | 78.8 | 249.0 | 12.6 | 23380 | 108.9 |
| N0Р80К0 | 50.1 | 2.8 | 78.6 | 60.9 | 176.8 | 13.3 | 27200 | 126.7 |
| N80Р80К0 | 53.8 | 2.7 | 108.0 | 71.1 | 213.1 | 14.2 | 23500 | 109.5 |
| N160Р80К0 | 64.1 | 2.4 | 154.8 | 79.6 | 228.5 | 20.7 | 34810 | 162.1 |
| N240Р80К0 | 64.4 | 3.0 | 147.8 | 76.2 | 273.4 | 18.5 | 33520 | 156.1 |
| N0Р160К0 | 47.3 | 2.5 | 49.3 | 45.7 | 138.5 | 9.3 | 27750 | 129.2 |
| N80Р160К0 | 60.9 | 3.1 | 145.5 | 82.1 | 251.8 | 15.5 | 30550 | 142.3 |
| N160Р160К0 | 65.7 | 3.0 | 152.0 | 81.1 | 244.3 | 13.5 | 29050 | 135.3 |
| N240Р160К0 | 66.6 | 3.1 | 194.1 | 101.5 | 260.9 | 14.5 | 26100 | 121.6 |
| N0Р240К0 | 49.9 | 2.0 | 43.4 | 44.6 | 135.4 | 8.2 | 29030 | 135.2 |
| N80Р24К0 | 64.9 | 2.5 | 144.6 | 75.5 | 227.6 | 17.3 | 31560 | 141.9 |
| N160Р240К0 | 66.9 | 2.1 | 130.6 | 66.7 | 197.2 | 14.6 | 35490 | 165.3 |
| N240Р240К0 | 68.1 | 3.5 | 164.3 | 67.4 | 188.7 | 15.1 | 34700 | 161.6 |
| N0Р0К80 | 45.4 | 3.3 | 45.8 | 48.4 | 124.6 | 8.2 | 21650 | 100.8 |
| N80Р80К80 | 55.1 | 2.7 | 125.4 | 85.9 | 254.5 | 11.2 | 22930 | 106.8 |
| N160Р160К80 | 61.8 | 3.5 | 117.6 | 56.4 | 197.2 | 14.0 | 37200 | 173.3 |
| N240Р240К80 | 68.9 | 3.8 | 153.3 | 63.6 | 200.8 | 14.2 | 35070 | 163.4 |
| N0Р0К160 | 49.1 | 3.1 | 54.2 | 37.4 | 118.5 | 9.9 | 30870 | 143.8 |
| N80Р80К160 | 60.7 | 3.2 | 137.1 | 67.5 | 241.0 | 12.3 | 32520 | 151.5 |
| N160Р160К160 | 61.9 | 3.0 | 189.6 | 81.7 | 263.4 | 13.4 | 39420 | 183.6 |
| N240Р240К160 | 62.9 | 2.2 | 171.2 | 70.0 | 211.4 | 11.2 | 24270 | 127.0 |
| GD 5% | 564.5 | |||||||
| GD 1% | 753.6 | |||||||
| GD 0.1% | 985.8 | |||||||
The yield increases up to 45.3% in increase of the rate of nitrogen from 0 to 160 kg N/ha applied separately. Fertilization with 240 kg N/ha results in a decrease of the yield compared to other variants, while towards the control the increase is with 8.9%. The same trend was established on a background P160 and P240. The differences are statistically well proven.
The yield increases in a direct ratio with the increase of fertilizer rate in nutrition with phosphorus separately. The greatest increase was obtained after fertilization with 240 kg P2O5 /ha – 2 9030 kg/ha, or with 35.2 percent more compared to the control. These results can be explained by the great responsiveness of root— and tuber crops to the phosphorus-potassium fertilization. This is confirmed by the variants with potassium fertilization, applied separately. Greater increase in the yield on a background of K80 and K160 was observed in the use of 160 kg N/ha.
Statistically proven impact of mineral fertilization on yield gives a reason to determine also the corresponding regression equations expressing the relationship between the rate of nitrogen at background PK and plant productivity /Figure 1/. The adequacy is very good in all equations (R2 = 0,63 — 0,96).
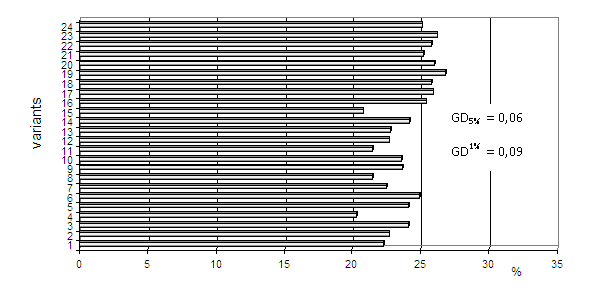
Figure 2. Dry matter content in tubers
The dry matter content in tubers varies averagely for the period from 20.3% after separately-fertilization with 240 kg N/da to 26.8% and 26.2% after fertilization N160P160 at a background 80 or 160 kg K2O/da /Figure 2/. The higher rates of nitrogen used both separately and on a background PK result in a decrease of the value of this index. These results demonstrate the higher effect of the combined mineral fertilization on the quality of the produce compared to the fertilization with phosphorus and potassium, applied separately with 80, 160 and 240 kg N/da.
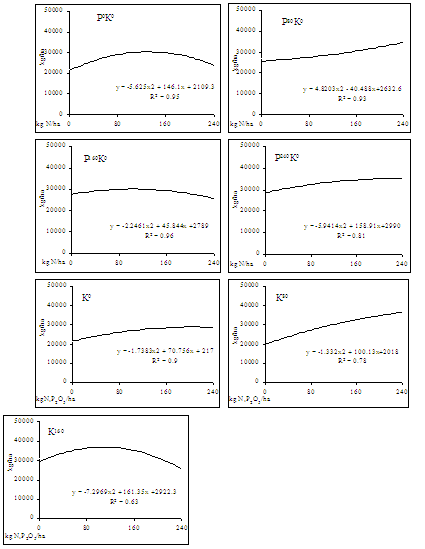
Figure 1. Amendment yield at different fertilization
CONCLUSIONS:
- The highest standard yield of potato is obtained after fertilization with N160P160K160 — 39420 kg/ha. The increase towards the control is 83.0%. The separately fertilization with nitrogen over 160 kg N/ha results in reduction of the standard yield. The effect of phosphorus fertilization on yield is the highest in a background 240 kg P2O5/ha, and of potassium fertilization – in a background of 160 kg K2O/ha.
- The equations of the curves expressing the relationship between rate of nitrogen, background PK and productivity of plants are determined by regression analysis. A trend towards decrease of dry matter in tubers with increase of nitrogen fertilizer rate applied both separately and on a background PK is established.
REFERENCES
- 1. Fedotova, M. C. [2003]. The conditions mineral nutrition, productivity and quality potatoes. Agrochemistry, № 2, 31-36
- 2. Atanasova, E. [2005]. Quality of the potato depending on the mineral fertilization. Soil science, agricultural chemistry and ecology., Years. XL, №1, 45-48
- 3. Dimitrov St., V. Blagoeva. [1995]. Effect of fertilization and some soil on accumulation of nitrate in potatoes. Scientific papers of the Agricultural University, Vol. 2, 223-228
- Dimitrov St. [1975]. Soil science and agricultural chemistry, №3
- Nacheva, E. [2004]. Rozhen – a new Bulgarian potato variety suitable for fresh consumption and processing. Lucrari stiintifice. Anale. Institutul de Cercetare – Dezvoltare Pentru Cartof si Sfecla de Zahar Vol. XXXI. Proceedings of EAPR Agronomy Section Meeting. Mamaia, Romania, June 23 – 27th 2004, Brasov, 57-65.
- Petkova, V., Peneva IS. [2002]. Effects of high temperature and drought on chlorophyll fluorescence parameters in varieties and breeding lines potatoes. Scientific papers of the Union of Scientists, vol. II, 75-82
- Nacheva, E. [2006]. Evaluation of the productivity components in potato breeding materials. J. Selekcia I semenarstvo. Plant breeding and seed production. Novi sad XII, Broj 3-4, 9-13
- Dimitrov St. [1971]. PhD Tesis, Plovdiv, 185[schema type=»book» name=»EFFECT OF MINERAL FERTILIZATION ON PRODUCTIVITY AND QUALITY OF EARLY POTATO» description=»The effect of mineral fertilization on the biological manifestations, yield and dry matter content in potato tubers form variety Nadejda suitable for early field production, was studied during three years in the “Maritsa“ Vegetable Crops Research Institute, Plovdiv on heavy leached meadow-cinnamon soil. A field experiment with increasing nitrogen rates: 0, 80, 160 и 240 kg/ha input separately and at background of phosphorus: 0, 80, 160 and 240 kg Р2О5/ha and chosen variants for potassium: 0, 80 and 160 kg К2О/ha is carried out in order to established the optimal rates and N:P:K proportions. Equations of the curved lines expressing the relationship between the rates and nitrogen, PK background and yield are found by regression analysis. The purpose of the study is to optimize the nutrient regime in potatoes — early field production for obtaining of high yields and produce with high biological value, satisfying the requirements of the organic agriculture.» author=»Boteva Hriska Manusheva» publisher=»БАСАРАНОВИЧ ЕКАТЕРИНА» pubdate=»2016-12-25″ edition=»euroasian-science.ru_25-26.03.2016_3(24)» ebook=»yes» ]